
Schematic for cfDNA extraction using a homobifunctional imidoester
Since its discovery in circulating blood seven decades ago, cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has become a highly focused subject in cancer management using liquid biopsy. Despite its clinical utility, the extraction of cfDNA from blood has many technical difficulties, including a low efficiency of recovery and long processing times. We introduced a magnetic bead-based cfDNA extraction method using.

cfDNA extraction through in situ formation of threedimensional
Circulating free DNA (cfDNA) (also known as cell-free DNA) are degraded DNA fragments released to body fluids such as blood plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. Typical sizes of cfDNA fragments reflect chromatosome particles (~165bp), as well as multiples of nucleosomes, which protect DNA from digestion by apoptotic nucleases. The term cfDNA can be used to describe various forms of DNA.

Circulating cellfree DNA (cfDNA) and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) are
The aim of the document, which is entitled "Biospecimen Evidence-based Best Practice for Cell-free DNA: Biospecimen Collection and Processing", is to improve the accuracy of cfDNA analysis in both basic research and the clinic by improving and harmonizing practices across institutions. Analysis of cfDNA from the bloodstream has been widely.

Conceptual framework of cellfree DNA (cfDNA) fragmentation analysis
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is a valuable biomarker for early detection, identification, and monitoring of various diseases. As a minimally invasive technique, liquid biopsy has gained attention as an alternative to tissue biopsy, overcoming limitations such as sampling bias and tissue heterogeneity. 1, 2 However, the analysis of cfDNA presents significant challenges because of its relatively low.
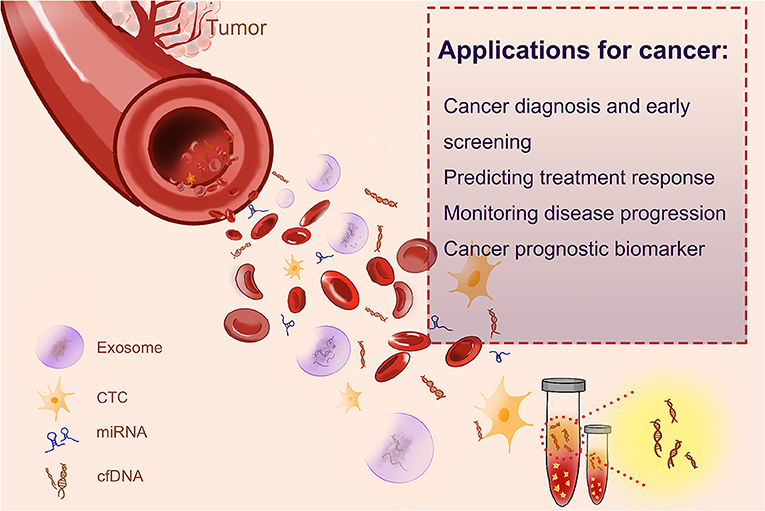
Frontiers CellFree DNA Hope and Potential Application in Cancer
1. cfDNA—Historical Perspective. Circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) are extracellular fragments of DNA present in body fluid that may be derived from both normal and diseased cells []. cfDNA molecules were discovered in the human circulatory system in 1948 by Mandel and Metais [].Seventeen years later, in 1965, Bendich et al. [] hypothesized that cancer-derived cfDNA was a determining factor.
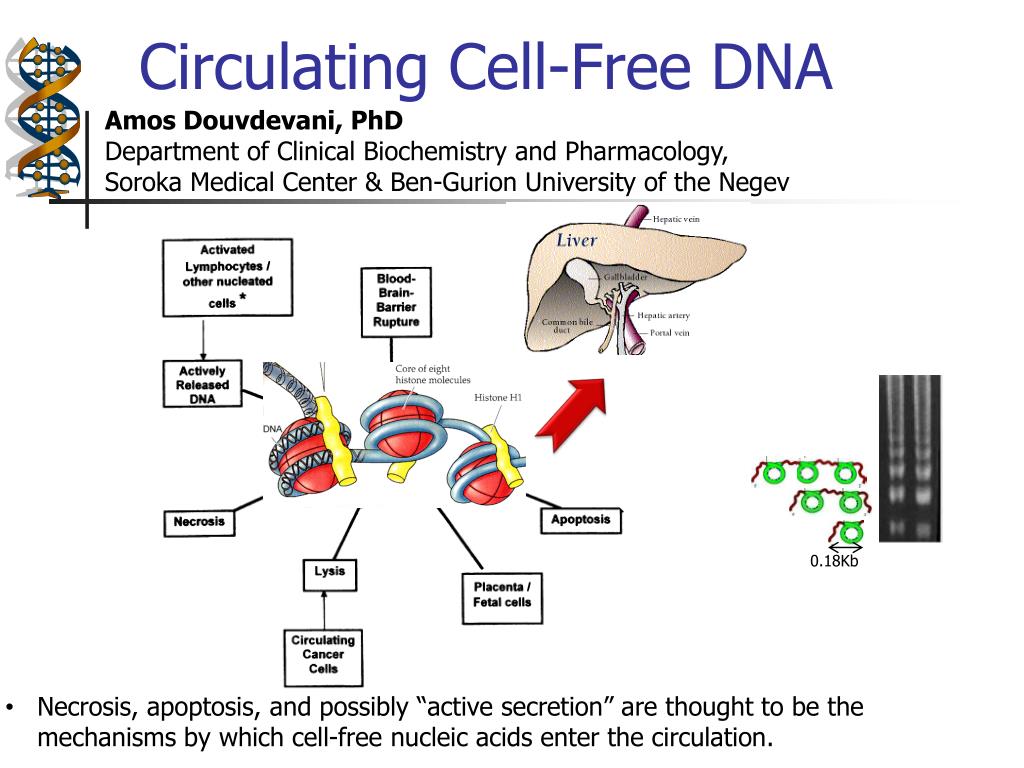
PPT Circulating CellFree DNA PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Learn more basics about Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) Extraction. Status of cfDNA and ctDNA research New liquid biopsy testing technology utilizing cfDNA as circulating biomarkers has been applied in clinical medicine with multiple FDA approved test on market, for example, detection of epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations with ctDNA in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)Read More

The optimal technique for cellfree DNA (cfDNA) analysis is chosen
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) serves as a valuable biomarker for early disease detection and monitoring. However, the use of cfDNA for analysis faces challenges owing to general low but variable abundance and fragmentation. Preanalytical factors, including cfDNA extraction, impact cfDNA quality and quantity. Efficient and robust cfDNA extraction is essential for reliable results in downstream.

The potential clinical scope of cfDNA profiling. (A) material
By adopting amine-conjugated magnetic beads, DMS-DNA complexes can be rapidly isolated from blood plasma. Using standard washing and eluting processes, we successfully extracted cfDNA from plasma within 10 min. This method yielded a 56% higher extraction efficiency than that of a commercial product (QIAamp kit).

Dna Extraction Techniques
Molecular Cancer (2022) Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) analysis represents a promising method for the diagnosis, treatment selection and clinical follow-up of cancer patients. Although its general.

Profiling disease and tissuespecific signatures in cell
Shown is the process of detecting fetal trisomy with the use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in maternal plasma. Fetal cfDNA derives from the turnover of placental tro-phoblasts and accounts for.

Epigentek Inc EpiQuik Circulating CellFree DNA (cfDNA) Isolation Easy
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) can be used as a liquid biopsy in neuro-oncology. New applications harnessing the biological patterns of cfDNA improved detection. This review will provide the basis to understand and use cfDNA biological signatures. Liquid biopsy, and cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in particular, have been intensively investigated for diagnostic.

Dna Extraction Process
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) are degraded DNA molecules/fragments that are released into the bloodstream by cells. These fragments, which can vary in length between 50 and 300 base pairs, are no longer confined or encapsulated inside a cell but circulating freely in the bloodstream. Hence it's called cell-free DNA.
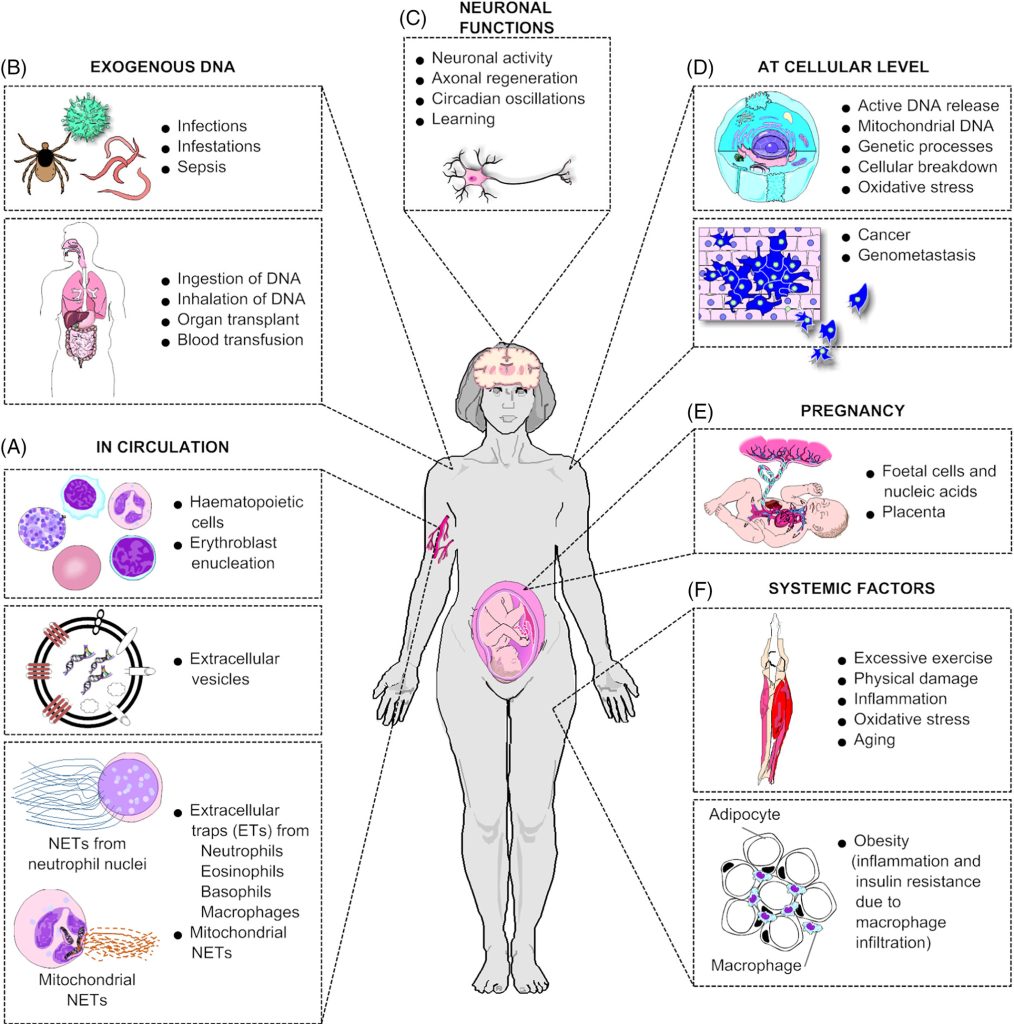
Cellfree DNA (cfDNA)Introduction, Properties, Applications Sciencevivid
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is a minimally invasive and real-time biomarker for the early detection, identification and monitoring of various diseases. Liquid biopsy has been investigated as a minimally invasive technique that can avoid the inherent shortcomings of tissue biopsy, such as sampling bias, tissue heterogeneity and difficulty in repetitive sample extraction [ 1 , 2 ].

Sequencing of Circulating Cellfree DNA during Pregnancy NEJM
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA) has become a comprehensive biomarker in the fields of non-invasive cancer detection and monitoring, organ transplantation, prenatal genetic testing and pathogen detection.

CellFree DNA and Apoptosis How Dead Cells Inform About the Living
Abstract. An increasing number of studies demonstrate the potential use of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) as a surrogate marker for multiple indications in cancer, including diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring. However, harnessing the full potential of cfDNA requires (i) the optimization and standardization of preanalytical steps, (ii) refinement of.

cfDNA (cellfree DNA) & cfDNA Extraction Basics & Development NVIGEN
Low yields of extracted cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from plasma limit continued development of liquid biopsy in cancer, especially in early-stage cancer diagnostics and cancer screening applications. We.