
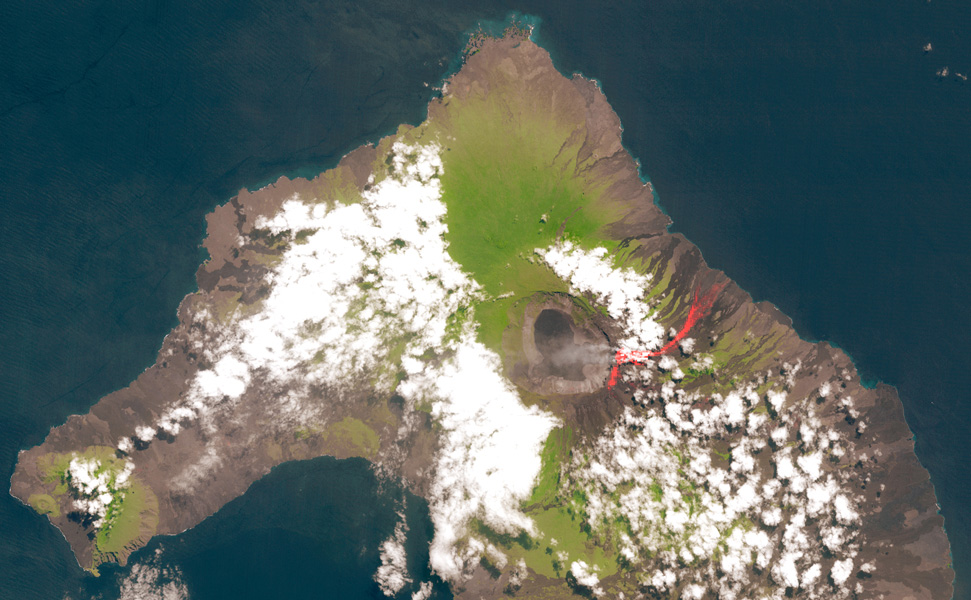
The Volcanic Eruption at Fagradalsfjall Special Tours
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid. Lava tubes can account for a large portion of shield volcano activity; for example, an estimated 58% of the lava forming Kīlauea comes from lava tubes.

Where Are Shield Volcanoes Found On Earth The Earth Images
These volcanoes can be hundreds of kilometers wide. Examples of shield volcanoes include: MAUNA LOA: Mauna Loa in Hawaii is the world's largest active shield volcano. From its base below sea level to its summit, it's also the tallest mountain in the world. FERNANDINA ISLAND: Fernandina Island is an active shield volcano in the Galapagos.
What are three examples of shield volcanoes? Socratic
Shield volcanoes have very gentle slopes of only a few percent that become even more gentle near the summit. The great width of these volcanoes relative to their height is the result of the low viscosities of erupted lavas that produce thin widespread lava flows, eruptions from both the summit and fissure vents on the volcano's flanks, and widening and subsidence along the summit and rift zones.

Shield Volcano Examples Worldwide YourDictionary
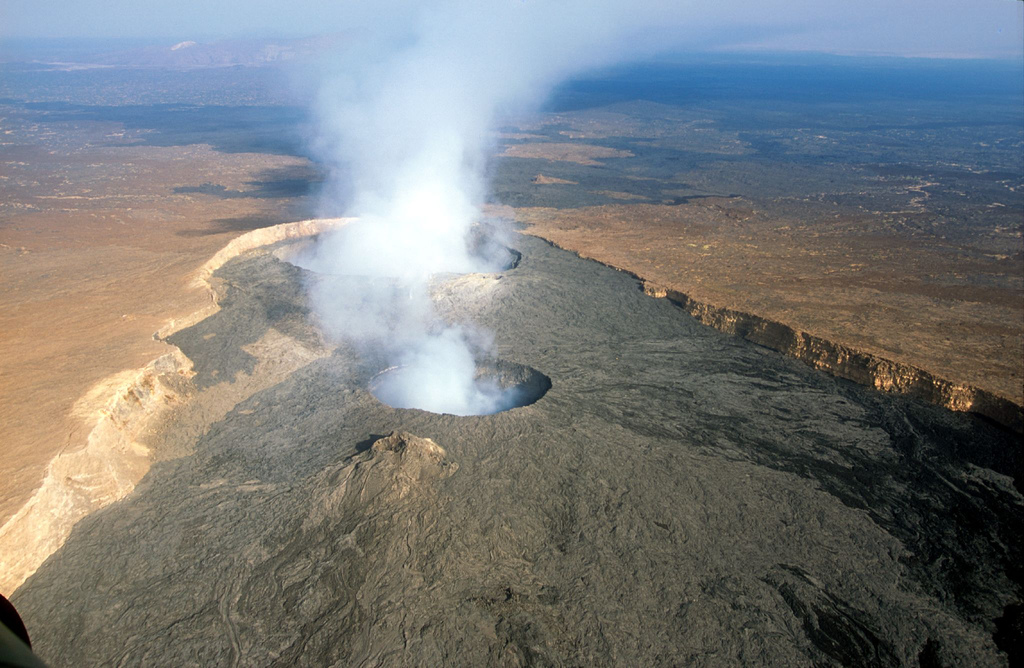
This list of shield volcanoes includes active, dormant and extinct shield volcanoes. Shield Volcanoes are one of the three types of volcanoes. They have a short cone shape, and have basaltic lava which means the lava has low viscosity (viscosity is a measure of the ability for a liquid to flow)

The Types of Eruptions That Shield Volcanoes Have Sciencing
It is mainly built from multiple layers of fluid lava flows. 2. How are shield volcanoes formed? Shield volcanoes form through effusive eruptions, where runny lava flows steadily and continuously from the volcano's vent. These flows gradually build up the shield-shaped structure over time.
/GettyImages-126940483-ML2-58ab18f73df78c345bd4541e.jpg)
Definition and Overview of Shield Volcanoes
Where a volcano produces low viscosity, runny lava, it spreads far from the source and forms a volcano with gentle slopes: a shield volcano. Most shield volcanoes are formed from fluid, basaltic lava flows. Mauna Kea and Mauna Loa are shield volcanoes. They are the world's largest active volcanoes, rising over 9 km above the sea floor around.
What is a Shield Volcano? Earth How
The shield volcano is an active volcano with a caldera that tends to erupt basalt lava. The name "shield volcano" originated from its Roman shield-like shape and is often broad and flatter than the other types of volcanoes. We want to hear what you have to say! Please use the comment form below and let us know what your thoughts are.

Learning Geology Volcanism and Types of Volcano
Finding an example of a shield volcano shouldn't be too hard: they're all around the world! Discover their names and locations with our extensive list.

Shield Volcanoes Martian Chronicles AGU Blogosphere
Profiles of shield volcanoes resemble that of a Roman warrior's shield having a gently sloping, convex-upward landform. Shield volcanoes are the largest known volcano type in the solar system. Olympus Mons on Mars is the largest mountain in the Solar System, rising 24 km above the surrounding plain, having a base which is more than 500 km in diameter, and rimmed by a cliff 6 km high.

Shield Volcano
Shield volcanoes are exactly what the nomenclature implies - very large, broad, shield-like structures that have a low aspect ratio (i.e., much wider than they are tall).. Two examples are the bimodal volcanoes of Newberry (Figure 15.8(B), 15.10(A)) and Medicine Lake in the subduction-related setting of the Cascades arc of western North.

Shield Volcanoes A Trip on the Lava Train Articles by MagellanTV
In volcano: Determinants of size and shape.the huge but gently sloping shield volcano Mauna Loa, for example, indicates a long record of eruption of fluid lava flows, while the beautiful, symmetrical shape of the stratovolcano Mount Fuji indicates a long record of moderately explosive eruptions from its summit that produce alternating layers of ash and lava.…

Shield Volcanoes (U.S. National Park Service)
For example, Mauna Loa, a shield volcano located on the "Big Island" of Hawai'i, is the world's largest active volcano. The fabled volcano accounts for more than 50 percent of the surface of the Big Island. Most commonly, shield volcanoes form during a single long-term eruption that can last decades, centuries, millennia, or more. For.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-556449987-56b6ac8a3df78c0b135b3fb1.jpg)
5 Different Ways to Classify Volcanoes
The composition of lava at shield volcanoes is mafic. Shield volcanoes are very large. For example, the Mauna Loa Volcano has a diameter of more than 112 kilometers (70 miles). The volcano forms a significant part of the island of Hawaii. The top of nearby Mauna Kea Volcano is more than ten kilometers (6 miles) from its base on the seafloor.

examples of composite volcanoes
The three main types of volcanoes are cinder cones, composite volcanoes (stratovolcanoes) and shield volcanoes. Lava domes are a common fourth type of volcano. However, there are other kinds of volcanoes, plus they are compound or complex volcanoes that have features of multiple types. For example, Trident Volcano in Alaska is a complex volcano.

Utah’s Three Types of Volcanoes
Shield Volcanoes. In this section, we review an example of a shield volcano and the hazards associated with such volcanoes. Shield volcanoes are typically the largest volcanoes on Earth and occur on the seafloor due to specific plate tectonic activity. Due to the properties of the magma that erupts from underneath the seafloor, the volcanoes.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-647383775-YS-58ab1a4f5f9b58a3c9a1204a.jpg)
Definition and Overview of Shield Volcanoes
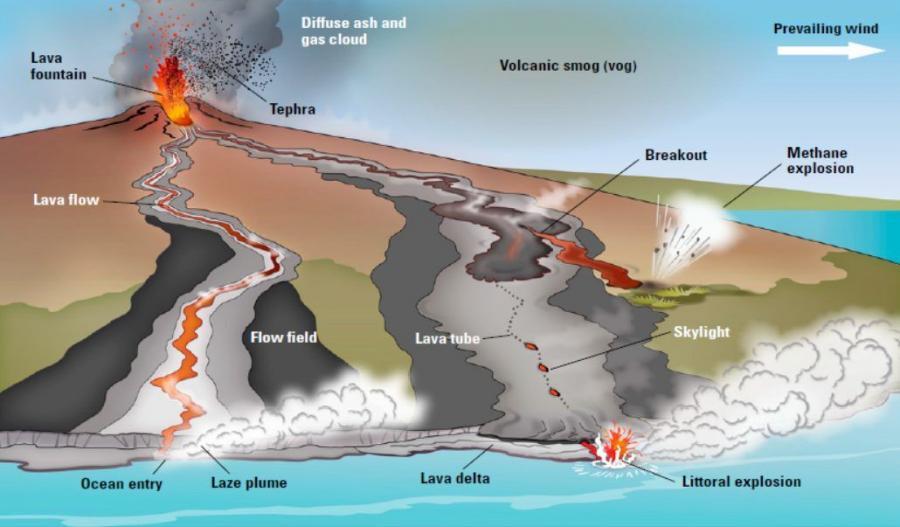
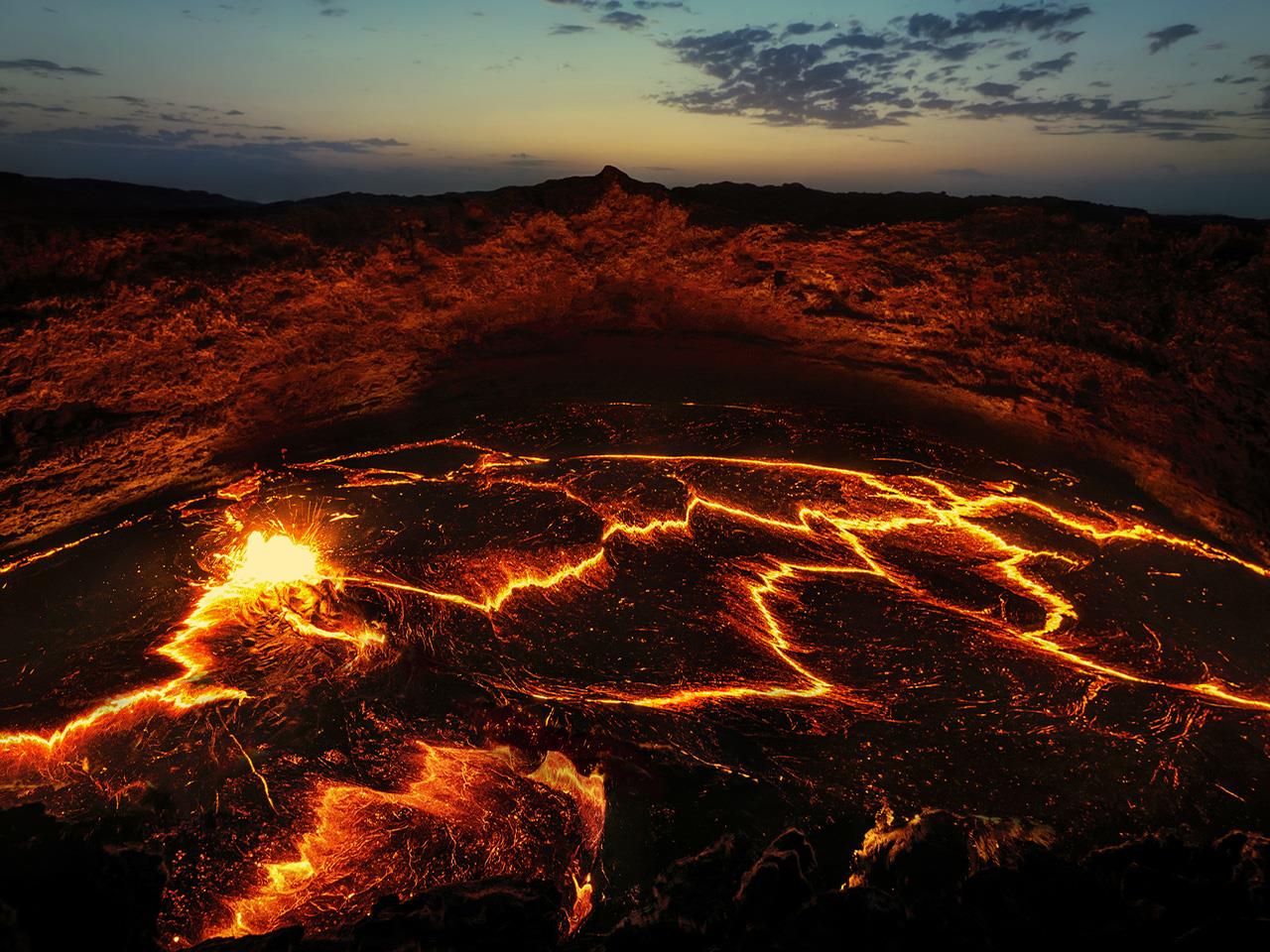
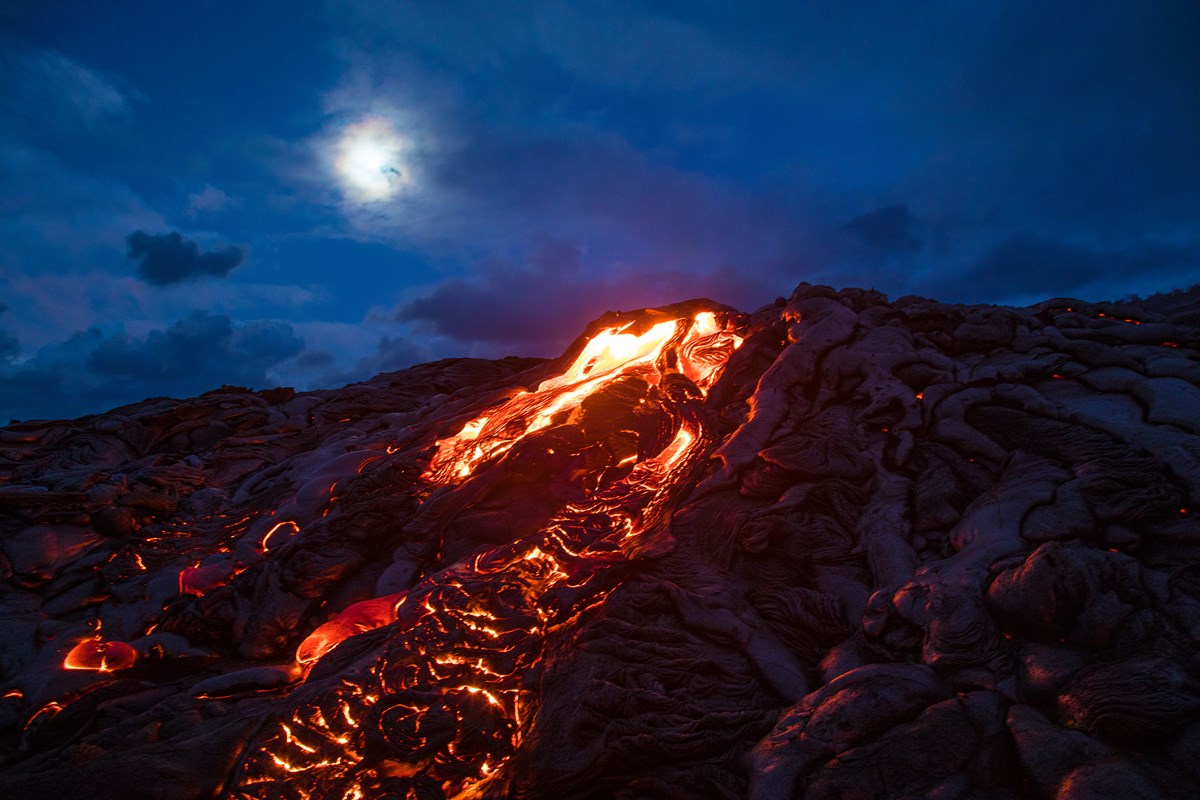
The lava flows from shield volcanoes is primarily of two types, pahoehoe -- pronounced "pah-hoy-hoy" -- and a'a (pronounced "ah-ah," said sharply). Both these types originate from surface eruptions, while a third type, pillow lava, is more likely to form from undersea eruptions. However, pillow lava can also be formed from pahoehoe lava that.