
Stratified Random Sampling Definition, Method and Examples
Stratified sampling is a method of sampling that involves dividing a population into homogeneous subgroups or 'strata', and then randomly selecting individuals from each group for study. The process of classifying the population into groups before sampling is called stratification.

Probability Sampling Definition, Methods and Examples
Stratified sampling is a sampling technique where the researcher divides or 'stratifies' the target group into sections, each representing a key group (or characteristic) that should be present in the final sample.For example, if a class has 20 students, 18 male and 2 female, and a researcher wanted a sample of 10, the sample would consist of 9.

PPT Stratified Sampling PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6015867
Oliver C. Robinson University of Greenwich, Department of Psychology and Counselling, London, UK Correspondence [email protected]. Pages 25-41 | Published online: 18 Nov 2013.. such as random sampling, convenience sampling, stratified sampling, cell sampling, quota sampling or a single-case selection strategy; and (4).

PPT Sampling PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2419622
Cluster sampling and stratified sampling are two sampling methods that break up populations into smaller groups and take samples based on those groups.. Practical Psychology began as a collection of study material for psychology students in 2016, created by a student in the field. It has since evolved into an online blog and YouTube channel.

PPT SAMPLING METHODS PowerPoint Presentation ID587453
Stratified Random Sampling is a sampling method (a way of gathering participants for a study) used when the population is composed of several subgroups that may differ in the behavior or attribute that you are studying. For example, you want to find out whether workers who did a lot of overtime work had higher performance scores. If you had.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Stratified-Random-Sampling-bfdd236e0ecf4a4c97aeec4c2a189740.png)
How stratified random sampling works, with examples (2022)
Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller subgroups known as strata. In stratified random sampling, or stratification, the.
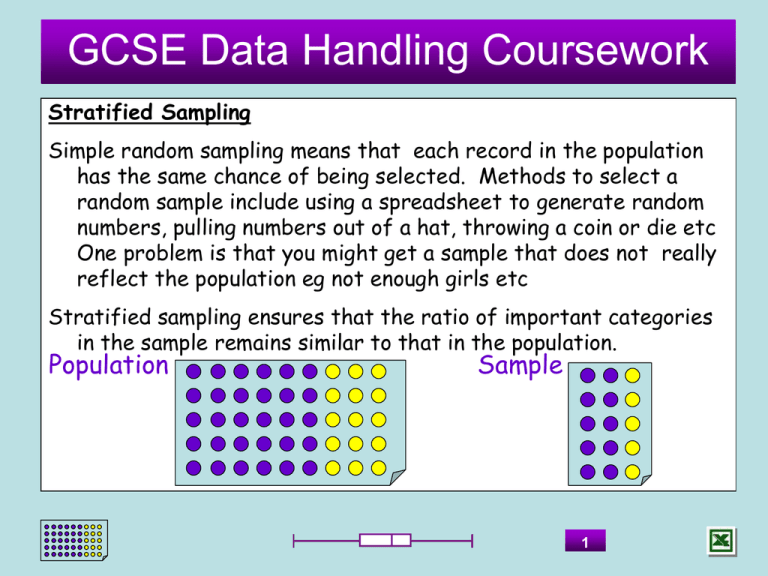
Stratified Sampling
Stratified random sampling allows researchers to obtain a sample population that best represents the entire population being studied by dividing it into subgroups called strata. This method of.

Stratified Sampling Definition, Advantages & Examples Statistics By Jim
Stratified random sampling involves separating the population into subgroups and then taking a simple random sample from each of these subgroups. For example, researchers may divide the population into subgroups based on race, sex, or age, and then take a simple random sample of each of these groups.
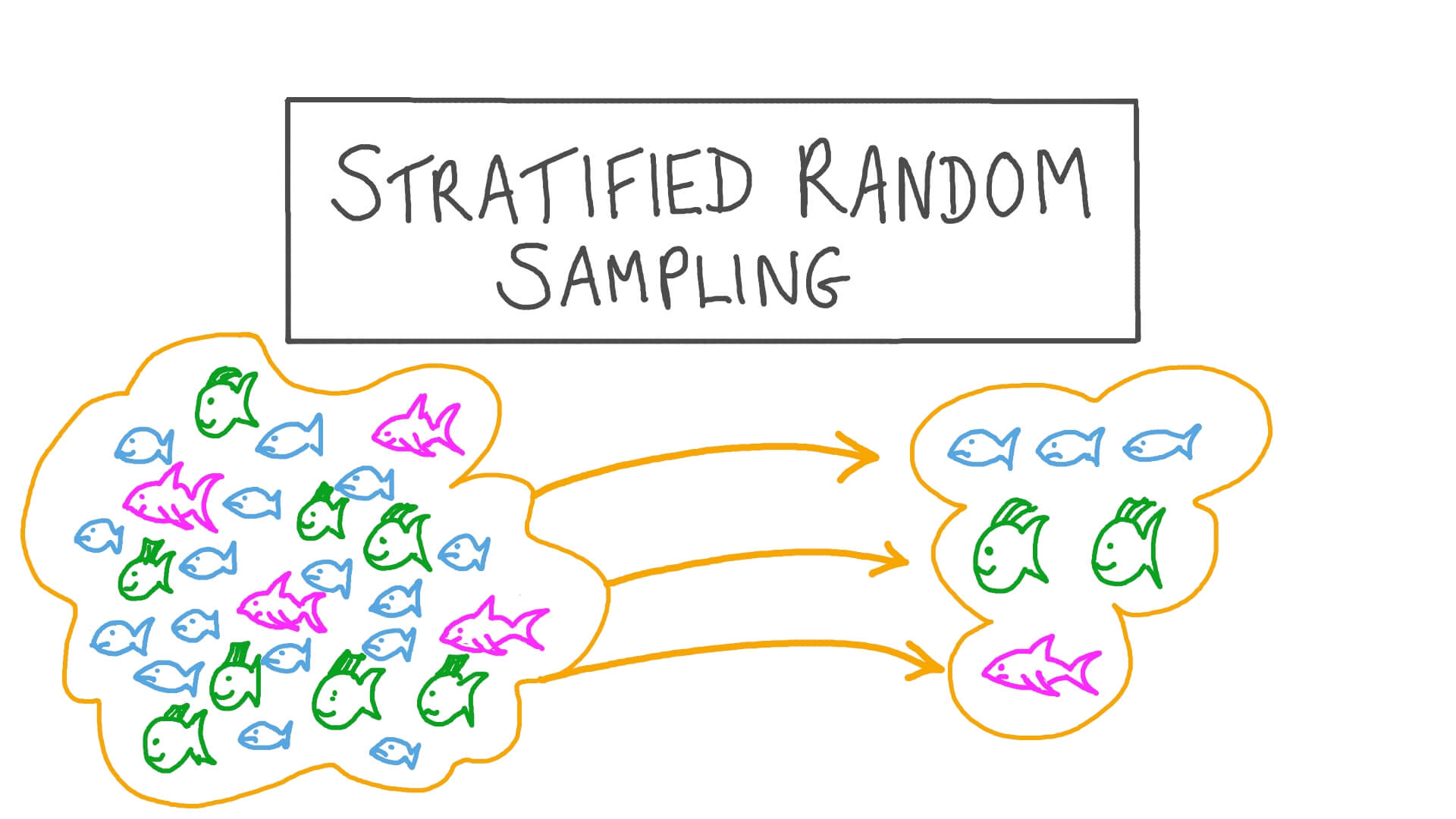
Stratified Sampling Example Vector Illustration Diagram
Psychology Scientific Investigation Stratified Sampling Stratified Sampling Have you heard of stratification? You might think of social stratification which is the separation and classification of people into groups based on varying qualities -- money, power, or status. Is stratification in sampling methods the same?

Cluster Sampling vs. Stratified Sampling What's the Difference?
A stratified sample is one that ensures that subgroups (strata) of a given population are each adequately represented within the whole sample population of a research study. For example, one might divide a sample of adults into subgroups by age, like 18-29, 30-39, 40-49, 50-59, and 60 and above. To stratify this sample, the researcher.

Pin on EPIDEMIOLOGY
Stratified sampling. In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations . Stratified sampling example. In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation ( stratum) independently.
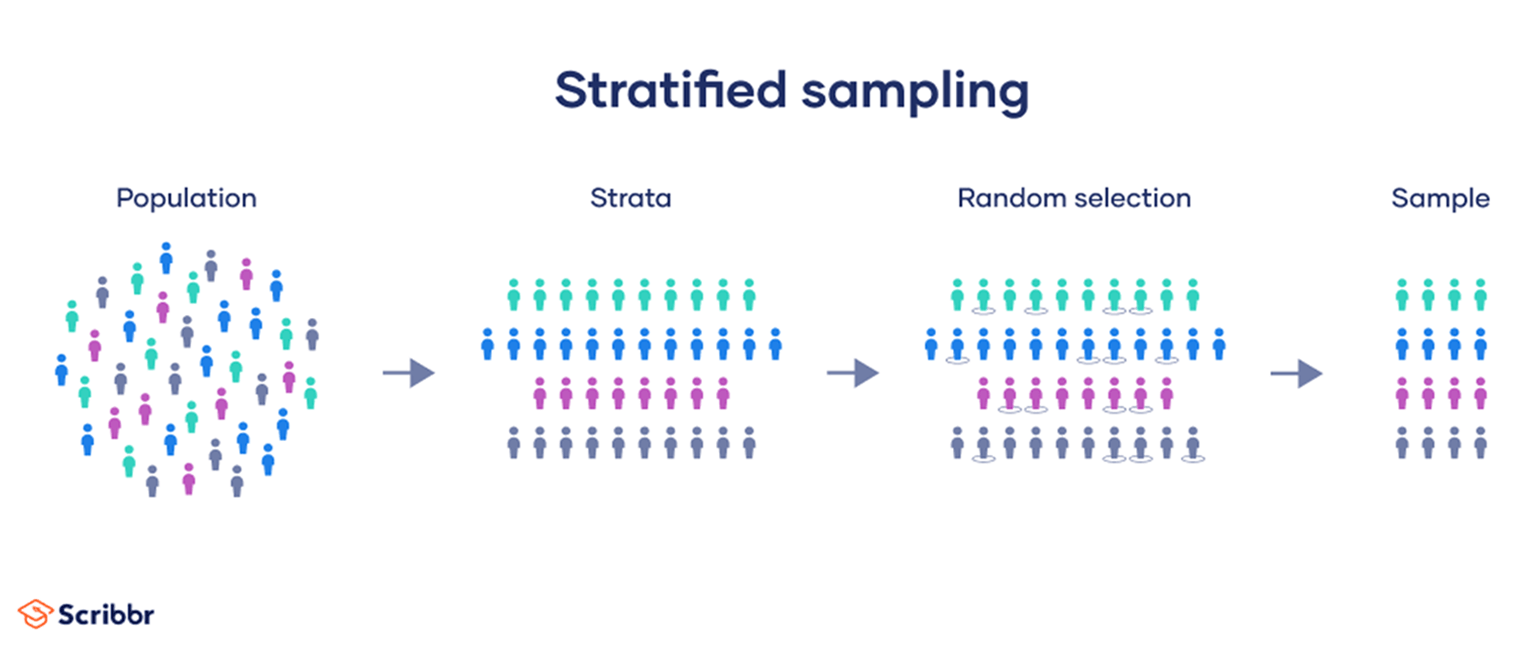
Stratified Sampling Definition, Guide & Examples
Stratified sampling is the best choice among the probability sampling methods when you believe that subgroups will have different mean values for the variable (s) you're studying. It has several potential advantages: Ensuring the diversity of your sample

Stratified sampling Variation Theory
7.1 Probability versus Non-Probability Sampling. Essentially all psychological research involves sampling—selecting a sample to study from the population of interest. Sampling falls into two broad categories. Probability sampling occurs when the researcher can specify the probability that each member of the population will be selected for the.

Description Stratified sampling example, vector illustration diagram. Research method
Sampling bias occurs when certain groups of individuals are more likely to be included in a sample than others, leading to an unrepresentative sample. Sampling bias results in biased samples of a population where all individuals were not equally likely to have been selected and thus do not accurately represent the entire group.

Sampling AO1 AO2 AO3 PSYCHOLOGY WIZARD
In stratified random sampling, a chance process (e.g., a random number generator) is used to select individuals, whereas in stratified systematic sampling an objective, orderly procedure is applied to choose individuals (e.g., listing all of the students within each major alphabetically and choosing every 10th case). Browse Dictionary
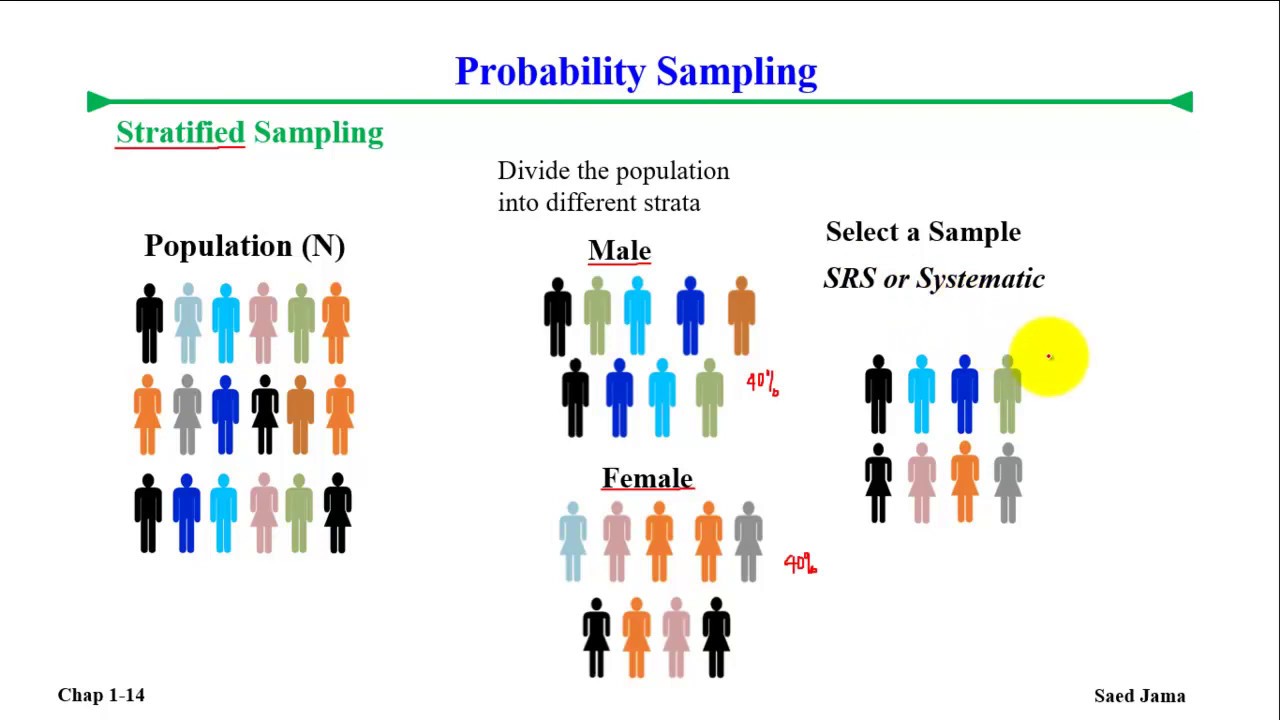
3.3. Stratified Sampling YouTube
Stratified Sampling Here the sampler divides or 'stratifies' the target group into sections, each showing a key characteristic which should be present in the final sample. Then each of those sections is sampled individually.